Understanding Logistic Regression and Naive Bayes
Coding the Logistic Regression and Naive Bayes classifier from scratch and analyzing the performance on identifying Ham vs Spam email.
The Coding
All the code was written in Python without using any of the pre-existing ML libraries such as tensorflow, sklearn, etc. The code can be found on my GitHub. The following are the highlights of the code:
- Implement the multinomial Naive Bayes algorithm for text classification described here:
- Implemented the discrete Naive Bayes algorithm with add-one laplace smoothing.
- Implement the MCAP Logistic Regression algorithm with L2 regularization.
- Used the SGDClassifier from scikit-learn for comparison.
The Experiments
Used the spam/ham used in the Metsis et al. paper @CEAS 2006.
I converted the text data into a matrix of features × examples (namely our canonical data representation), using the following approaches.
- Bag of Words model: I used a vocabulary having w words (the set of all unique words in the training set) and represent each email using a vector of word frequencies (the number of times each word in the vocabulary appears in the email).
- Bernoulli model: As before I used a vocabulary having w words and represent each email (training example) using a 0/1 vector of length w where 0 indicates that the word does not appear in the email and 1 indicates that the word appears in the email.
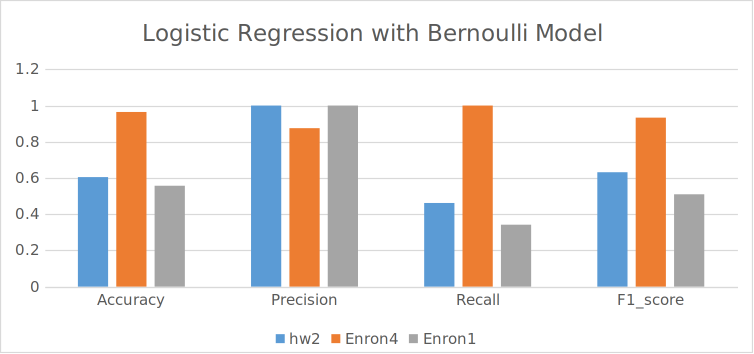
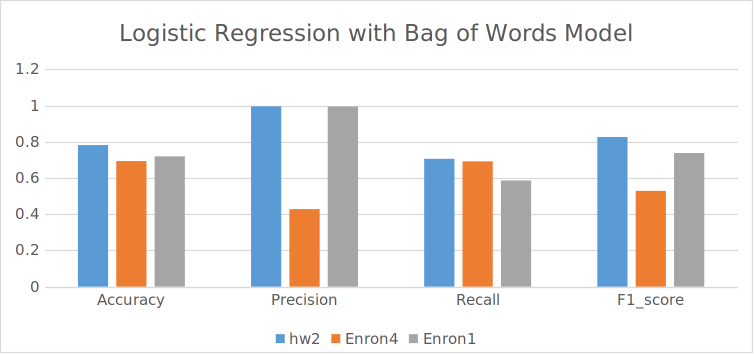
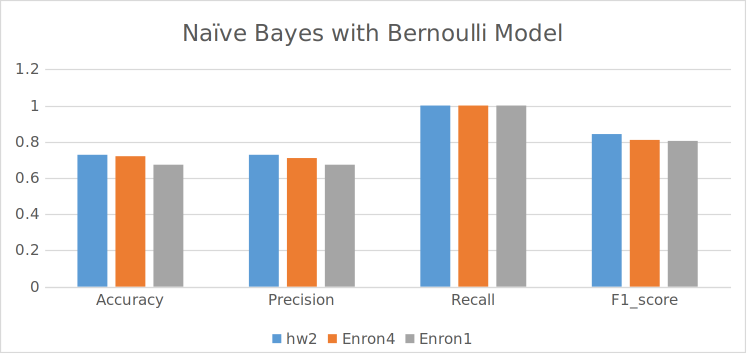
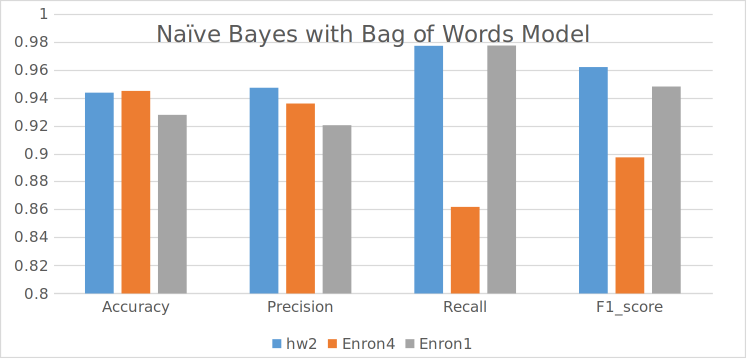
The Learnings
I like to categorize my learnings into two categories: The Profound and The Subtle. The Profound are the key questions that were answered through this project. The Subtle could be an intuition I had, insight I discovered or a clever python hack I learnt from this project. For example, print statement has a parameter called end which can be used to change the default newline character to something else.
The Profound
Q1. Which data representation and algorithm combination yields the best performance (mea- sured in terms of the accuracy, precision, recall and F1 score) and why? Naïve bayes yields the best performance with the bag of words model (~94% accuracy) because it has the frequency of the words which gives serves as better feature values than the simple 0/1 values in the Bernoulli model. The logistic regression also performs well with the bag of words model but not as well as the naïve bayes. The bag of words model is better than the Bernoulli model because it has more information about the words in the email.
Q2. How does the size of the vocabulary impact the performance of the classifiers? The size of the vocabulary impacts the performance of the classifiers. The performance of the classifiers decreases as the size of the vocabulary increases. Since there are more features that are added to the model, the model becomes more complex and the curse of dimensionality comes into play.
Q4. How does the performance of the classifiers compare to the performance of the scikit-learn classifiers?
The performance of the classifiers is comparable to the performance of the scikit-learn classifiers. The scikit-learn classifiers are faster.
The Subtle
- The SGDClassifier from scikit-learn is very fast and gives good results. The libraries are optimized for runtime and are very efficient.
- A simple classifier like Naive Bayes can give very good results on text data. The frequency of the words is a good feature value for the classifier.